The Achilles Tendon orcalcaneal tendonorheel cord, is the big entwinedensemble of fibrous tissuesthat is located at the back of the lower leg and connects the calf muscles(gastrocnemius and soleus muscles) to the heel bones (calcaneal tuberosity on the calcaneus).It is the largest and the strongest tendon in the human body. The Achilles tendon endures a lot of stress and pressure in the normal day-to-day activities, such as, walking, jumping, running, as well as athletic activities. However, a rupture in the Achilles tendon can be caused among the people of any age group, but most ruptures are caused during the age of 30-50, among the people who are very physically active or are professional athletes.
The tears in the tendon fibers can result in a partial or total disruption of the tendon. If you hear sudden pop sound at the back of the calf, then the condition might need instant medical care.
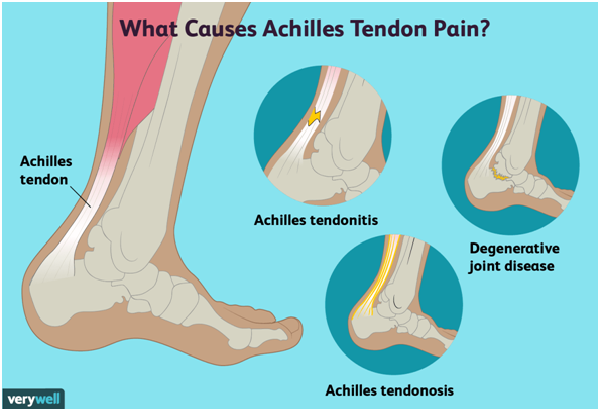
Achilles Tendon: Causes
Achillis Tendonitis is normally caused by repetitive and intense pressure on the Achilles Tendon. The structure of the Tendon weakens with age, making it more prone to the injury. There are two main types of Tendonitis:
The first type of Tendonitis, Non-insertional Achilles Tendonitis, usually affects the younger adults. It causes pain and swelling as the small slits of the middle fibers of the tendon begins to disrupt.
The second type of Tendonitis, Insertional Achilles Tendonitis, can occur at any age, even to people who are not very physically active. The pain is caused due to additional bone development at the spot where the Tendon meets the heel bone.
Achilles Tendon: Symptoms
Achilles Tendonitis can weaken the tendon and can make the tendon more prone to the rupture, which may require an immediate surgical repair. The symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis are:
- Stiffness, aching or swelling within the tendon. Pain can be at its intensity upon waking up in the morning and worsening during the day due to increased activities. The pain would occur at the back of the leg or near the heel.
- Powerful penetrating pain when the sides of the tendon are squeezed. However, when the back of the tendon is touched or squeezed there is considerably less pain.
- Enlargement or growth of nodules may arise in the spots where the tissue is injured. The patient will experience difficulty in bending the affected foot.
Achilles Tendon: Treatment
After the Achillis Tendonitis is diagnosed by the doctor through your medical history, visible symptoms and X-ray results, it is important to get the right treatment.Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. If the injury is not very intense, the doctor will ask you to take considerable amount of rest, frequent ice compression at the affected area, intake of pain relieving drugs, special exercises that you can do on your own to strengthen the calf muscle, physiotheraphy, orthotic shoes (to lift your heel).
If the above treatment is not of much relief then the foot doctor might recommend surgery. Some of the surgical methods may include: surgery to extend the gastrocnemius (calf muscle) decline or surgery to remove the excess bone growth and to repair the tendon.
It is very important to seek out a podiatrist if you believe you have an injury in the Achilles region, because further damage could result in severe complications that would make being mobile difficult, if not impossible.

