 Developing a non-healing wound can be one of the most serious and devastating complications for a diabetic patient. These wounds or open sores are also called diabetic ulcers, and they frequently occur on the foot. Diabetic foot ulcers are prone to infections, and this puts patients at a higher risk of hospitalization and need for surgery or amputation.
Developing a non-healing wound can be one of the most serious and devastating complications for a diabetic patient. These wounds or open sores are also called diabetic ulcers, and they frequently occur on the foot. Diabetic foot ulcers are prone to infections, and this puts patients at a higher risk of hospitalization and need for surgery or amputation.
 Making healthy food, checking your blood sugar, taking time to be active, keeping up with doctor's appointments, and taking medicines are some of the things diabetic patients manage. However, through this busy schedule, the feet are the last thing to be remembered but daily diabetic foot care will help prevent diabetic foot complications.
Making healthy food, checking your blood sugar, taking time to be active, keeping up with doctor's appointments, and taking medicines are some of the things diabetic patients manage. However, through this busy schedule, the feet are the last thing to be remembered but daily diabetic foot care will help prevent diabetic foot complications.
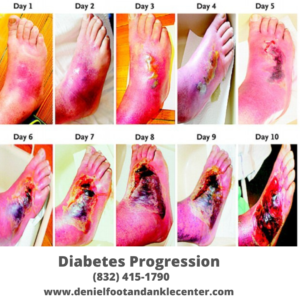 People with diabetes experience foot problems often and are always in fear of the unknown, the worst being one in the reality of losing a foot, leg, or toe. Managing diabetes or glucose levels will keep your feet healthy.
People with diabetes experience foot problems often and are always in fear of the unknown, the worst being one in the reality of losing a foot, leg, or toe. Managing diabetes or glucose levels will keep your feet healthy.
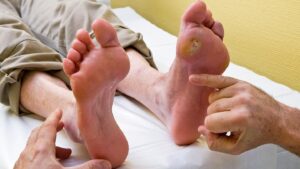 Have you ever taken off your socks or shoes and saw blood, and had no idea how it happened? Well, 15 percent of patients with diabetes suffer from diabetic foot ulcers. A diabetic foot ulcer is an open injury or sore generally situated on the lower part of the foot. It starts from normal factors such as taking an extra-long walk or having a new pair of shoes. The ulcer starts as a small blister or callus on the foot, then the problem progresses.
Have you ever taken off your socks or shoes and saw blood, and had no idea how it happened? Well, 15 percent of patients with diabetes suffer from diabetic foot ulcers. A diabetic foot ulcer is an open injury or sore generally situated on the lower part of the foot. It starts from normal factors such as taking an extra-long walk or having a new pair of shoes. The ulcer starts as a small blister or callus on the foot, then the problem progresses.
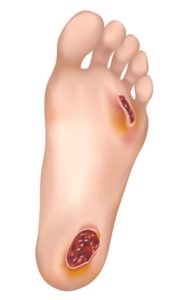 It is common for people with diabetes to have foot problems. It is scarier when you think of losing a foot, toe, or leg especially when you know someone who has lost any limps to diabetes complications. However, with diabetic foot care, managing your glucose levels, and regular visits to a podiatrist for diabetics, chances of experiencing diabetic foot problems are reduced. Half of the diabetic patients experience nerve damage, mostly happening in their legs and feet.
It is common for people with diabetes to have foot problems. It is scarier when you think of losing a foot, toe, or leg especially when you know someone who has lost any limps to diabetes complications. However, with diabetic foot care, managing your glucose levels, and regular visits to a podiatrist for diabetics, chances of experiencing diabetic foot problems are reduced. Half of the diabetic patients experience nerve damage, mostly happening in their legs and feet.

What Is Wound Care?
A wound occurs when the internal tissue is exposed to the skin, due to an external or internal injury. Most people conduct wound care at home but consult a podiatrist for proper diabetic wound care. Seek diabetic foot ulcer treatment from a podiatrist to avoid the development of complications that may lead to hospitalization of patients. Foot ulcers for diabetic patients can lead to amputation if wound care treatment is not well done.
Wound care treatment
There are basic principles for wound care; ensure you wear protective gear when attending to a wound.
- Hemostasis – Applied to significant wounds with bleeding to stop the bleeding. The bleeding is stopped by reducing the bleeding or aiding the hemostasis process. Some of the techniques used include elevation, suturing, pressure, or tourniquet.
- Cleaning the wound – This promotes healing and reduces the infection. Five main steps of wound cleaning are
- Disinfect all around the wound without getting detergents and alcohol into the injured area.
- Decontaminate by removing foreign bodies from the wound.
- Debride any tissues around the wound.
- Wet the wound with saline if no obvious contamination can be seen. Saline should be stored in a sterile container.
- For heavily soiled wounds, open foot fractures, puncture wounds, and animal bites use antibiotics. It is advisable to introduce antibiotics at the first sign of wound infection.
- Skin closure – This aids the wound healing using skin adhesive strips, tissue adhesive glue, sutures, and staples are some skin closure techniques for the edge of the wounds.
- Dress the wound – This effectively reduces contamination and infection of the injury. When dressing, the first layer should be saline-soaked, followed by an absorbent material layer to attract wound exudates. Finally, use a soft gauze to secure the dressing in place. It is advisable to get tetanus immunization if not already done.
Diabetic foot ulcer treatment
Patients using insulin are at a higher risk of developing a foot ulcer. Also, for overweight people or people who use alcohol and tobacco the risk is high. A diabetic foot ulcer develops due to lack of feeling in the foot, trauma, foot deformities, and irritation. Pain may not be felt by diabetic patients. Seek podiatric medical care for diabetic foot ulcer treatment. This reduces the risk of wound infection leading to amputation. To appropriately treat a diabetic foot ulcer, ensure that you:
- Prevent infections.
- Offload or take the pressure off the wound.
- Regularly remove dead tissue and skin from the wound.
- Apply dressing and medication to the ulcer.
- Manage blood glucose under tight control to avoid ulcer infection.
- Clean the wound daily and dress it.
- Ensure adequate circulation on the ulcerated area with the help of a podiatrist.
- Surgical treatment – If other ulcer treatments are not effective, surgical management may be used to correct deformities and shave or excision the bone.
The time needed for healing depends on different factors including wound care management used and the diabetic foot ulcer treatment used.
Over at DeNiel Foot and Ankle Center located in Houston, Texas, and covering surrounding areas like Cypress, and Katy, TX. Ejodamen Shobowale, DPM and her highly skilled staff provide personalized comprehensive care for all your podiatry and sport medicine needs. Whether the issue is foot-related like hammertoes, or toenail fungus or involves pain in the heel , nerves, or joints, Dr. Sho, as she is fondly called, can get you back on your feet in no time.